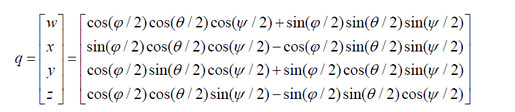使用程序实现父子坐标系的转换
除了直接用static_transform_publisher外,当然可以在程序中实现两个坐标系的转换,以经典的乌龟追乌龟程序为参考,它的tf树是这样的
现在我们写一个这样的程序:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
void poseCallback(const turtlesim::PosePtr& msg)
{
static tf::TransformBroadcaster br;
tf::Transform transform;
transform.setOrigin( tf::Vector3(0,0, -0.24) ); //子坐标系相对父坐标系的位移
//子坐标系相对父坐标系的旋转,可以用欧拉角和四元数两种形式
tf::Quaternion q;
q.setRPY(0, 0, 0);
//tf::Quaternion q(qx,qy,qz,qw);
transform.setRotation(q);
br.sendTransform(tf::StampedTransform(transform, ros::Time::now(), "turtle1", "robot_base")); //父坐标系在前,子坐标系在后
}
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
ros::init(argc, argv, "camera_base_tf");
ros::NodeHandle node;
ros::Subscriber sub = node.subscribe("/turtle1/pose", 10, &poseCallback);
ros::spin();
return 0;
}
我们订阅乌龟1的位姿话题/turtle1/pose,在回调函数里定义tf广播和变换的参数,最后发送。这里只能用回调函数的形式,因为在main函数里只能发一次,无法建立父子坐标系的关系。tf::broadcaster类的sendTransform函数中,把父子坐标系交换,只会交换tf树中的位置,坐标关系还是原来的,所以必须使用Transform::inverse ()函数.
使用程序获得坐标系在另一坐标系中的坐标
1 |
|
这个程序获得的是乌龟2在乌龟1坐标系中的坐标
先运行roslaunch turtle_tf turtle_tf_demo.launch,这是ROS自带的一个tf演示程序,然后马上运行上面的程序。我们会看到乌龟1不动,乌龟2向前者移动,如果运行程序太慢,乌龟2就停止了,二者没有相对运动就捕捉不到tf话题上的消息了

同时我们的程序会输出下面内容1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12[ INFO] [1551530137.681192434]: x: -1.394780
[ INFO] [1551530137.681317271]: y: -3.510608
[ INFO] [1551530137.681352733]: z: 0.000000
[ INFO] [1551530137.781891361]: x: -1.221200
[ INFO] [1551530137.781970030]: y: -3.391552
[ INFO] [1551530137.782007398]: z: 0.000000
[ INFO] [1551530137.982427762]: x: -1.018356
[ INFO] [1551530137.982512261]: y: -3.122349
[ INFO] [1551530137.982559203]: z: 0.000000
...... //忽略
显然从图中能看出乌龟2在乌龟1的坐标系中初始坐标x,y肯定都是负值。随着运动,xy的绝对值越来越小,最终两个乌龟重合,xy都成为0。
程序分析
waitForTransform函数的原型有两个,我们用的这个是:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9bool Transformer::waitForTransform
(
const std::string & target_frame,
const std::string & source_frame,
const ros::Time & time, //The time at which to transform
const ros::Duration & timeout, //How long to block before failing
const ros::Duration & polling_sleep_duration = ros::Duration(0.01),
std::string * error_msg = NULL
)const
功能:函数阻塞直到能进行坐标系转换或者时间timeout截止,返回值表示是否成功。函数不会throw,如果给error_msg传变量,它会在函数出错时记录错误信息。
一般用前四个参数就行了,如果开始没有坐标系转换,会报错 “turtle1” passed to lookupTransform argument target_frame does not exist 。如果又有了转换,程序可以正常运行。因为网络问题,如果timeout为0,那会直接报错失败,如果设置太小,也可能捕捉不到转换。使用tf_echo就会发现它要等一点时间才会输出结果,这是一样的道理。
lookupTransform函数的原型也有两个,我们用的是:1
2
3
4
5
6
7void Transformer::lookupTransform
(
const std::string & target_frame,
const std::string & source_frame,
const ros::Time & time, //某时间的变换,0表示最近的变换
StampedTransform & transform
)const
功能:获得两坐标系之间的转换,也就是赋值给tf::StampedTransform对象
还有函数canTransform(),这个函数纯粹就是判断用的,也能记录错误信息,但不能指定阻塞时间。
技巧 1
1 | std::string tf_error; |
其他有用的函数
tf::Transformer类的重要函数
std::string Transformer::allFramesAsString() constA way to see what frames have been cached Useful for debugging.bool Transformer::frameExists (const std::string & frame_id_str) constCheck if a frame exists in the tree.
void Transformer::getFrameStrings ( std::vector< std::string > & ids ) constA way to get a std::vector of available frame ids.getParent
1 | bool Transformer::getParent ( const std::string & frame_id, |
Fill the parent of a frame.
- frame_id The frame id of the frame in question
- parent The reference to the string to fill the parent Returns true unless “NO_PARENT”
- transformQuaternion()