ros的地图坐标系: 左下角为原点, 向右为x正方向, 向上为y正方向, 角度以x轴正向为0度, 逆时针为正
cartographer的地图坐标系: 坐标系右下角为原点, 向上为x正方向, 向左为y正方向角度正方向以x轴正向为0度, 逆时针为正。左上角为坐标的最大值
cartographer的像素坐标系: 左上角为原点, 向右为x正方向, 向下为y正方向
Cartographer中,Eigen::Array2i指像素坐标, Eigen::Vector2f指地图坐标.
在函数MapLimits::GetCellIndex和GetCellCenter可以看到cartographer的地图坐标系和像素坐标系的转换
MapLimits的几个重要成员函数1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26// 计算物理坐标点的像素索引
// 返回的这个点是栅格的中心点,因此,栅格点(grid_point)是一个格子的中心
Eigen::Array2i GetCellIndex(const Eigen::Vector2f& point) const
{
// Index values are row major and the top left has Eigen::Array2i::Zero()
// and contains (centered_max_x, centered_max_y). We need to flip and
// rotate.
return Eigen::Array2i(
common::RoundToInt((max_.y() - point.y()) / resolution_ - 0.5),
common::RoundToInt((max_.x() - point.x()) / resolution_ - 0.5));
}
// 根据像素索引计算物理坐标
Eigen::Vector2f GetCellCenter(const Eigen::Array2i cell_index) const
{
return {max_.x() - resolution() * (cell_index[1] + 0.5),
max_.y() - resolution() * (cell_index[0] + 0.5)};
}
// 判断像素索引是否在栅格地图内
bool Contains(const Eigen::Array2i& cell_index) const
{
return (Eigen::Array2i(0, 0) <= cell_index).all() &&
(cell_index <
Eigen::Array2i(cell_limits_.num_x_cells, cell_limits_.num_y_cells))
.all();
}
Insert函数
1 | void ProbabilityGridRangeDataInserter2D::Insert( |
输入的range_data在LocalTrajectoryBuilder2D::AddRangeData的最后部分,已经计算了misses和returns(注意不是 hit) 先看传感器数据类型RangeData的定义:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9struct RangeData {
Eigen::Vector3f origin; // 当次扫描测量时激光雷达的位置
// PointCloud就是 vector<Eigen::Vector3f>
// 扫描到的hit点与miss点
PointCloud returns;
PointCloud misses;
};
// 对 2D SLAM, 第三个元素为0
// typedef std::vector<Eigen::Vector3f> PointCloud;
所谓的hit点是指在该点上扫描到了障碍物,该点所在的栅格单元就发生了一次hit事件。miss点所在的位置上并没有检测到障碍物,只是以传感器的最远有效距离记录下坐标而已。
之前获得的带有时间戳的点云类型TimedPointCloud并没有区分hit点和miss点 ,该数据类型只是将原始数据中的距离和扫描角度信息转换为空间点的坐标。
看到这里,参数grid的来源已经记不清了,往回查会发现,它的根源是ActiveSubmaps2D::AddSubmap的添加子图里,也就是Submap2D的构造函数,最终是CreateGrid函数
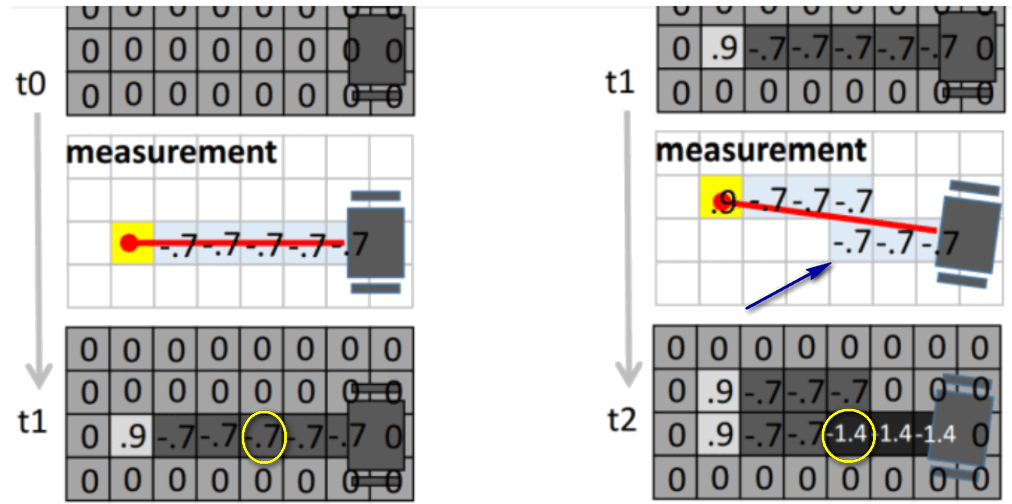
CastRays
从扫描得到的距离信息转换为栅格的hit或者miss事件的过程称为RayCasting,函数原型1
2
3
4void CastRays(const sensor::RangeData& range_data,
const std::vector<uint16>& hit_table,
const std::vector<uint16>& miss_table,
const bool insert_free_space, ProbabilityGrid* probability_grid)
分成三部分来分析1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14// 不必关注细节,实现当前grid map边界的扩展,让它能够覆盖雷达的所有扫描数据
// 根据return, misses调整,因为新的scan加入,可能会导致地图变大
GrowAsNeeded(range_data, probability_grid);
// 这部分和 ActiveSubmaps2D::CreateGrid 对比阅读
const MapLimits& limits = probability_grid->limits();
// 构建一个分辨率更好的 Maplimits,分辨率除以1000,提高RayCasting的精度
const double superscaled_resolution = limits.resolution() / kSubpixelScale;
const MapLimits superscaled_limits(
// 地图的x和y方向上的最大值max和原来的一样
superscaled_resolution, limits.max(),
// 地图格数扩展为原来的1000倍
CellLimits(limits.cell_limits().num_x_cells * kSubpixelScale,
limits.cell_limits().num_y_cells * kSubpixelScale) );
1 | // 获取激光射线的起点在精细栅格中的索引,记录在begin对象 |
更新时,仅需查表可获得更新后的结果,而无需临时进行乘法运算
处理misses,它有两部分: origin和hit之间的栅格;激光超出max_range的栅格1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19// 处理射线起点到hit点之间的栅格,来源还是上面的 range_data.returns
// 查找miss_table更新占用概率。这里的begin和end都是精细栅格下的索引
for (const Eigen::Array2i& end : ends)
{
std::vector<Eigen::Array2i> ray =
RayToPixelMask(begin, end, kSubpixelScale);
for (const Eigen::Array2i& cell_index : ray)
probability_grid->ApplyLookupTable(cell_index, miss_table);
}
// 处理超出max_range的miss点,来源是 range_data.misses
// 同样认为射线起点到miss点之间的栅格发生的都是miss事件
for (const sensor::RangefinderPoint& missing_echo : range_data.misses)
{
std::vector<Eigen::Array2i> ray = RayToPixelMask(
begin, superscaled_limits.GetCellIndex(missing_echo.position.head<2>()),
kSubpixelScale);
for (const Eigen::Array2i& cell_index : ray)
probability_grid->ApplyLookupTable(cell_index, miss_table);
}RayToPixelMask函数实在太复杂了,知道原理即可: 使用 Bresenham 画线的方法,获取激光原点到点云之间直线的所有点坐标,前面的精细化分辨率是为了这里的画线更精确
一条射线穿过很多cell,有的cell从对角穿过,有的只穿过一个小角落,虽然它们都是穿过,但是穿过的观测量不同,从对角穿过对这个cell的空闲概率的提升显然作用更大,而只穿过一个小角落显然贡献很小。
对于从对角穿过的cell,就有很多小的sub-cell落在原来的cell中,sub-cell数(记为n)越多,贡献就越大(其实就是对cell这个栅格的概率重复算了n次),而对于从小角落穿过的cell,sub-cell数就很少了.
ApplyLookupTable
查表来更新栅格单元的占用概率1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24// Multiple updates of the same cell will be ignored until
// FinishUpdate() is called. Returns true if the cell was updated.
// cell_index是将要更新的栅格单元索引,table是更新过程中将要查的表。
bool ProbabilityGrid::ApplyLookupTable(const Eigen::Array2i& cell_index,
const std::vector<uint16>& table)
{
DCHECK_EQ(table.size(), kUpdateMarker);
// 然后通过 cell_index 计算栅格单元的存储索引,获取对应的空闲概率存储值
// 并确保该值不会超出查找表的数组边界。
const int flat_index = ToFlatIndex(cell_index);
// 其实是 Grid2D类的成员: vector<uint16> correspondence_cost_cells_;
uint16* cell = &(*mutable_correspondence_cost_cells())[flat_index];
if (*cell >= kUpdateMarker)
return false;
// 通过父类的接口记录下当前更新的栅格单元的存储索引flat_index
mutable_update_indices()->push_back(flat_index);
// 通过查表更新栅格单元
*cell = table[*cell];
DCHECK_GE(*cell, kUpdateMarker);
// 通过父类标记cell_index所对应的栅格的占用概率已知
mutable_known_cells_box()->extend(cell_index.matrix());
return true;
}
CastRays结束,最后的是FinishUpdate()1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11// 主要就是减去 kUpdateMarker
void Grid2D::FinishUpdate() {
while (!update_indices_.empty())
{
DCHECK_GE(correspondence_cost_cells_[update_indices_.back()],
kUpdateMarker);
// ComputeLookupTableToApplyCorrespondenceCostOdds 加上了kUpdateMarker做更新标志,这里再减去
correspondence_cost_cells_[update_indices_.back()] -= kUpdateMarker;
update_indices_.pop_back();
}
}