旋转
有旋转向量、四元数和旋转矩阵三种表示方法,在Eigen里用前两种进行定义,这样参数少,可以转化为第三种。
牢记下面这张图,根据《视觉SLAM十四讲》总结: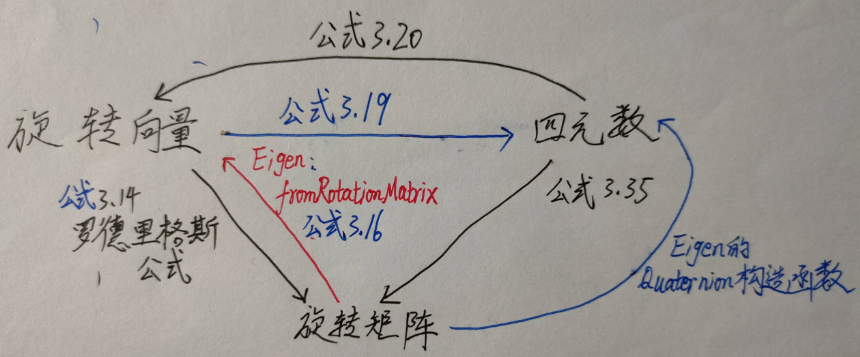
使用的是模板类:class Eigen::AngleAxis< Scalar >,这被称为角轴表示法,顾名思义给定旋转角度和旋转轴即可。其创建方式符合Eigen的原则,传入数据类型作为模板参数。旋转角度以弧度表示,旋转轴为Vector类型的向量,注意向量必须要被归一化(vec.normalized()即可)。Eigen中也预先定义好了AngleAxisd和AngleAxisf两种方便使用。
参考:基于eigen实现欧拉角(RPY), 旋转矩阵, 旋转向量, 四元数之间的变换
1 | Vector3f v1 = Vector3f::UnitX(); |
Quaternion是四元数表示法,Quaternion的构造是标准Eigen格式:数据类型作为模板参数+构造参数,而且重载了多个构造函数,因此可以方便地从角轴、旋转矩阵等数据类型进行构造。
Eigen提供了Quaternionf和Quaterniond方便使用。Quaterniond的初始化:1
2
3
4
5Eigen::Quaterniond q1(x, y, z, w);
Eigen::Quaterniond q2(Vector4d(x, y, z, w));
Eigen::Quaterniond q2(Matrix3d(R));
在Quaternion内部的保存中,虚部在前,实部在后。
如果以第一种方式构造四元数,则实部是x,虚部是[y,z,w]。 对于第二种方式,则实部是w,虚部是[x,y,z]; 对于第三种方式,则是用3x3的旋转矩阵初始化四元数。
所以最常用是 Eigen::Quaterniond q1(w, x, y, z); ,四个数的传入顺序是w、x、y、z,对应w+xi+yj+zk。
Eigen::Quaterniond 不能使用cout
Identity(): 返回一个表示单位旋转的四元数w(): 返回四元数中的w分量。 同理 x(), y(), z()是返回相应的分量。
coeffs(): 返回四元数的四个数,可以对其进行索引[]获取值。 需要注意的是返回顺序是x、y、z、w,和构造函数的不同
toRotationMatrix() 将当前Quaternion对象转换为3×3的旋转矩阵。另外,没有fromRotationMatrix()函数,只能用构造函数传入旋转矩阵
slerp():对两个四元数进行球面线性插值(Spherical linear interpolation,通常简称Slerp),是四元数的一种线性插值运算,主要用于在两个表示旋转的四元数之间平滑差值。
欧拉角 —— 旋转矩阵
可以让三个AngleAxis相乘:1
2
3
4
5
6// 参数顺序和 static_transform_publisher 的一致
Eigen::Vector3f angle(roll, pitch, yaw);
Eigen::Matrix3d rotation;
rotation = Eigen::AngleAxisd(angle[0], Eigen::Vector3d::UnitZ()) *
Eigen::AngleAxisd(angle[1], Eigen::Vector3d::UnitY()) *
Eigen::AngleAxisd(angle[2], Eigen::Vector3d::UnitX()) ;
这样计算的结果和每个AngleAxisf转换成旋转矩阵后再相乘得到的结果是相同的
四元数 —— 旋转矩阵
其实这样更简单,我们可以直接从tf2_ros::Buffer和geometry_msgs::TransformStamped直接获得四元数1
2
3
4
5
6Eigen::Quaterniond quaternion(transform.transform.rotation.w,
transform.transform.rotation.x,
transform.transform.rotation.y,
transform.transform.rotation.z
);
Eigen::Matrix3d rotation = quaternion.matrix();
平移
采用Eigen标准构造原则,构造示例如下:1
2
3
4Translation<float,2>(tx, ty)
Translation<float,3>(tx, ty, tz)
Translation<float,N>(s)
Translation<float,N>(vecN)
多个平移合并用乘号而不是加号,需要注意。和旋转相比,它的成员函数也相对少一些:
x():获取平移的x分量(可修改)
y():获取平移的y分量(可修改)
z():获取平移的z分量(可修改),注意,千万不要对一个二维的Translation获取z分量,否则直接会运行报错
vector()&.translation():返回当前平移的向量表示(可修改),可以索引[]获取各分量
1 | Translation2d t1(1,4); |
计算特征值与特征向量
构造一个EigenSolver,然后分别调用其成员函数.eigenvalues()、.eigenvectors()即可获得特征值与特征向量。
1 |
|
输出结果并不是我们平时熟悉的形式,而是1
2
3
4
5
6
7(4,0)
(1,0)
(-2,0)
(-0.666667,0) (-0.666667,0) (-0.333333,0)
(0.666667,0) (-0.333333,0) (-0.666667,0)
(-0.333333,0) (0.666667,0) (-0.666667,0)
实际特征值是4,1,-2. 4对应的特征向量分别为(-0.666667, -0.666667,-0.333333)