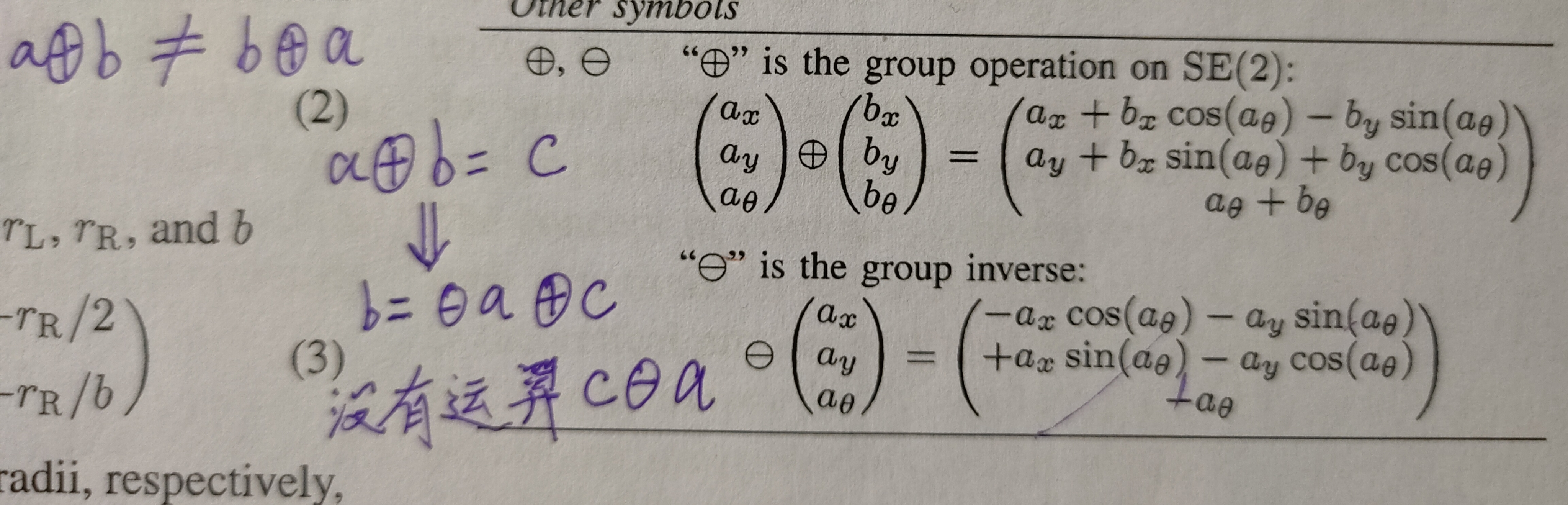目前所用的机器人模型是圆形, 在通用代价地图里定义:robot_radius: 0.26, 而不是footprint参数. 但是注意TEB里用的是Point类型.
指定footprint的数组元素时, 点如果太多, 可以换行。 机器人的轮廓可能是不规则的polygon, 但它的运动中心永远是(0, 0), 顺时针和逆时针规范都支持。 这应该是局部坐标系决定的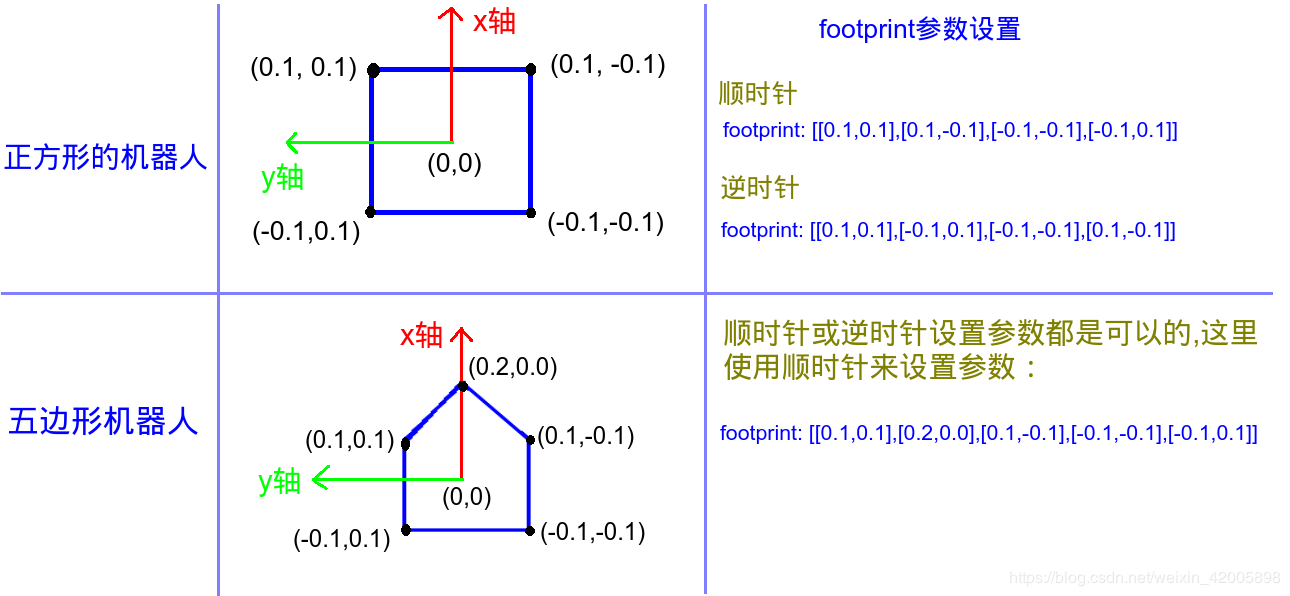
现在分析源码中对footprint参数的处理, Costmap2DROS的构造函数里有一句: setUnpaddedRobotFootprint(makeFootprintFromParams(private_nh));, 先看括号里的函数
makeFootprintFromParams
1 | std::vector<geometry_msgs::Point> makeFootprintFromParams(ros::NodeHandle& nh) |
函数检查通用代价地图的yaml里是否定义了footprint和robot_radius参数。 前者优先, 如果footprint已经定义了, 就把它做轮廓, 不再处理robot_radius. 我目前用的是robot_radius, 所以再看makeFootprintFromRadius1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16std::vector<geometry_msgs::Point> makeFootprintFromRadius(double radius)
{
std::vector<geometry_msgs::Point> points;
// Loop over 16 angles around a circle making a point each time
int N = 16;
geometry_msgs::Point pt;
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
{
double angle = i * 2 * M_PI / N;
pt.x = cos(angle) * radius;
pt.y = sin(angle) * radius;
points.push_back(pt);
}
return points;
}
这其实是把圆形处理成了一个正十六边形, 把顶点的坐标都放到容器里. 这个容器最终就是setUnpaddedRobotFootprint的参数。 打开rviz放大, 会看到它是一个十六边形。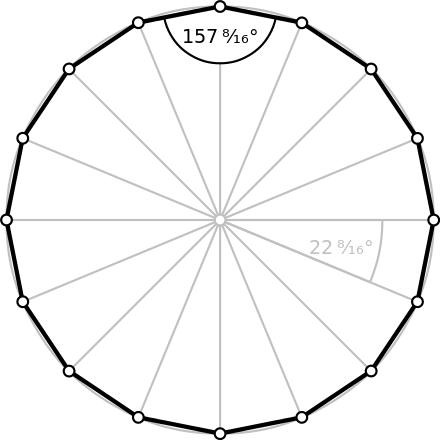
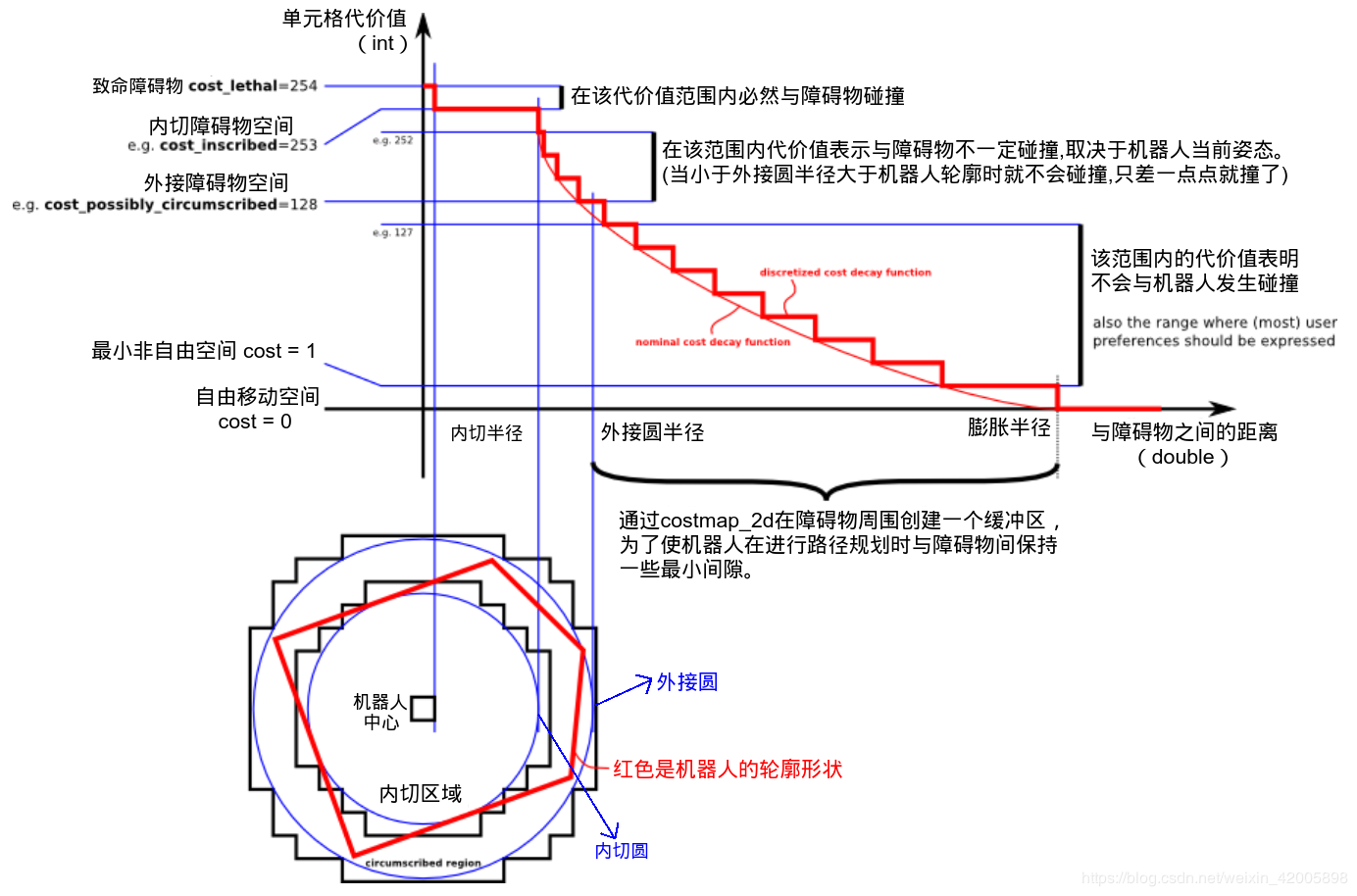
所以对于圆形轮廓机器人, 内接圆和外接圆的半径是不同的, 因为正十六边形的外接圆半径是内接圆半径的1.01959倍
setUnpaddedRobotFootprint
1 | void Costmap2DROS::setUnpaddedRobotFootprint(const std::vector<geometry_msgs::Point>& points) |
setUnpaddedRobotFootprint主要是对padded_footprint_赋值, 和setFootprint函数
footprint_padding_只用于reconfigureCB, 可以不看. padFootprint就是处理padding的情况, 但我们的footprint_padding参数为0, 所以也不看了.
当话题上收到footprint时, 回调函数会将接收到的footprint根据参数footprint_padding_的值进行膨胀, 得到膨胀后的 padded_footprint_, 传递给各级地图。
调用了这个函数的还有setUnpaddedRobotFootprintRadius回调函数 和 setUnpaddedRobotFootprintPolygon回调函数, 前者对应footprint_radius的参数值做的话题, 后者对应footprint_topic的参数值做的话题
1 | void LayeredCostmap::setFootprint(const std::vector<geometry_msgs::Point>& footprint_spec) |
calculateMinAndMaxDistances很重要, 它可求得内外圆的半径。footprint 无论是局部代价地图还是全局代价地图得到,两个半径的计算结果都一样。 对于固定的机器人,干脆将两个半径设置为固定值,省得计算。
这里的plugin就是全局和局部代价地图里定义的plugins成员, 别忘了MoveBase里有两个代价地图, 对plugin的添加在Costmap2DROS的构造函数里.
每一层都调用了onFootprintChanged, 但是只有膨胀层覆盖了基类函数, 也就是InflationLayer::onFootprintChanged(), 这个在另一篇文章分析. 其它层没有覆盖, 还是调用的Layer类的空函数virtual void onFootprintChanged() {}
机器人轮廓之所以能在导航时也行走, 原因在updateMap1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24void Costmap2DROS::updateMap()
{
if (!stop_updates_)
{
// get pose in global frame of costmap
tf::Stamped < tf::Pose > pose;
if (getRobotPose (pose))
{
double x = pose.getOrigin().x(),
y = pose.getOrigin().y(),
yaw = tf::getYaw(pose.getRotation());
layered_costmap_->updateMap(x, y, yaw);
geometry_msgs::PolygonStamped footprint;
footprint.header.frame_id = global_frame_;
footprint.header.stamp = ros::Time::now();
transformFootprint(x, y, yaw, padded_footprint_, footprint);
footprint_pub_.publish(footprint);
initialized_ = true;
}
}
}
逻辑不复杂, padded_footprint_就是上面的十六变形的Point容器, transformFootprint是更新机器人行走时的轮廓, 原理和里程计解算类似.
footprint_pub_发布的话题就是/move_base/local_costmap/footprint
相关话题 (不是参数)
footprint, 类型geometry_msgs/Polygon, 由move_base订阅, 但没有发布者。
/move_base/global_costmap/footprint和/move_base/local_costmap/footprint话题是机器人轮廓, 可以直接获得。
Padding机制
Padding机制为机器人和障碍物之间提供了额外的距离, 打开rqt_reconfigure调整全局代价地图的参数footprint_padding, 膨胀层和障碍层会变化, 效果和调整参数inflation_radius和cost_scaling_factor相同。
调整局部代价地图的footprint_padding, 机器人轮廓会成比例放大和缩小。 如果确实需要改变这个参数, 两个代价地图的都要改变。
话题 footprint_radius 和 polygon_footprint
这个和padding是不同的机制, 用话题的方式在线更改机器人的轮廓, 适用于机器人更换货架而导致轮廓改变的情况。
原因在源码中的这一段, footprint_radius是自己加的, 注意全局和局部代价地图的相应话题都只发布一次
所以可以看到move_base(实际在costmap_2d) 订阅/footprint_radius 和 footprint,但没有发布者
1 | private_nh.param(topic_param, topic, std::string("footprint")); |
两个回调函数都是调用函数setUnpaddedRobotFootprint, 对于radius的情况, 也就是圆形底盘, 还是把圆按正十六边形处理。
可以用命令测试,现实中由调度端实现:1
2
3
4
5rostopic pub -1 /move_base/local_costmap/footprint_radius std_msgs/Float32 '0.34'
rostopic pub -1 /move_base/global_costmap/footprint_radius std_msgs/Float32 '0.34'
rostopic pub -1 /move_base/local_costmap/polygon_footprint geometry_msgs/Polygon '[ [-0.3, 0.3], [0.3, 0.3], [0.3, -0.3], [-0.3, -0.3] ]'
rostopic pub -1 /move_base/global_costmap/polygon_footprint geometry_msgs/Polygon '[ [-0.3, 0.3], [0.3, 0.3], [0.3, -0.3], [-0.3, -0.3] ]'
TEB中的处理
footprint是多边形, 每增加一条边, 就会增加TEB计算时间。设置和通用代价地图里相同1
2type: "polygon"
vertices: [[-0.26,0], [-0.240209, 0.099498], [-0.183848,0.240209], [0,0.26], [0.099498,0.240209], [0.5662,0.240209], [0.5662,-0.240209], [0.099498,-0.240209], [0,-0.26], [-0.183848,-0.240209], [-0.240209, -0.099498] ]
内切圆半径和外切圆半径的计算原理
计算footprint的内切圆半径和外切圆半径, 用到点到线段的距离, 计算方法是两个向量的点积等于一个向量在另一个向量的投影乘以另一个向量的模。看函数distanceToLine
点到线段的三种情况如下:
1 | /* 作用:计算点到线段的距离 |