1 | // 局部的子目标 (transformed plan最后一个元素) |
参数global_plan_overwrite_orientation为True时,执行estimateLocalGoalOrientation(), 将未来一段的规划的姿态角的平均值返回为估计的局部目标姿态
transformed_plan.back()就是所谓的 local goal ,但是遇到需要终点转弯时,local goal的朝向不是最终的goal的朝向,仍然是规划的
1 | // 局部的子目标 (transformed plan最后一个元素) |
参数global_plan_overwrite_orientation为True时,执行estimateLocalGoalOrientation(), 将未来一段的规划的姿态角的平均值返回为估计的局部目标姿态
transformed_plan.back()就是所谓的 local goal ,但是遇到需要终点转弯时,local goal的朝向不是最终的goal的朝向,仍然是规划的
time elastic band(时间橡皮筋)从elastic band算法(1993年提出)优化而来。TEB的初始轨迹是全局路径传来的transformed_plan,中间插入N个控制橡皮筋形状的路径点(机器人位姿),在点与点之间定义时间差,转换为明确依赖于时间的轨迹,从而实现对机器人的实时控制。由于其模块化的形式,该方法可以扩展目标函数和约束。
TEB的创新在于考虑了动态约束和增加时间信息,如有限的机器人速度和加速度,将规划问题用加权多目标优化框架表示,也是一个bundle adjustment问题。在实时应用中,在线对全局路径进行大规模的计算往往是不可行的,TEB大多数目标函数是局部(local)的,因为它们依赖于一些邻近的中间 configurations。TEB的这种局部性会生成一个稀疏系统矩阵,才可以实现快速有效的大规模优化。作者写第一篇论文时(2012),把约束表示为一个分段连续、可微的代价函数,到了下一篇论文(2013),改成了使用g2o的图优化方法(利文伯格法)。
路径(Path)与轨迹(Trajectory)区别在于,轨迹包含了时间信息。所以TEB算法里老用Trajectory这个词。
目标函数的梯度可以理解为作用在弹性带上的外力。
TEB的目标函数分为两类:
目标函数依赖的参数只取决于邻近位姿的子集。比如:
但是最快和最短路径是例外,显然是因为它们需要全局地依赖于所有的参数。
TEB同时考虑原始路径的via-point约束和避开障碍。这两个目标函数相似,不同之处在于via-point吸引路径,而障碍物排斥路径。
约束用到了几个顶点(待优化变量),对应的就是几元边。 比如速度约束用到了两个位姿和一个时间差,是三元边。 加速度约束就是五元边。 障碍约束和via-point就是一元边。非完整运动学约束是二元边。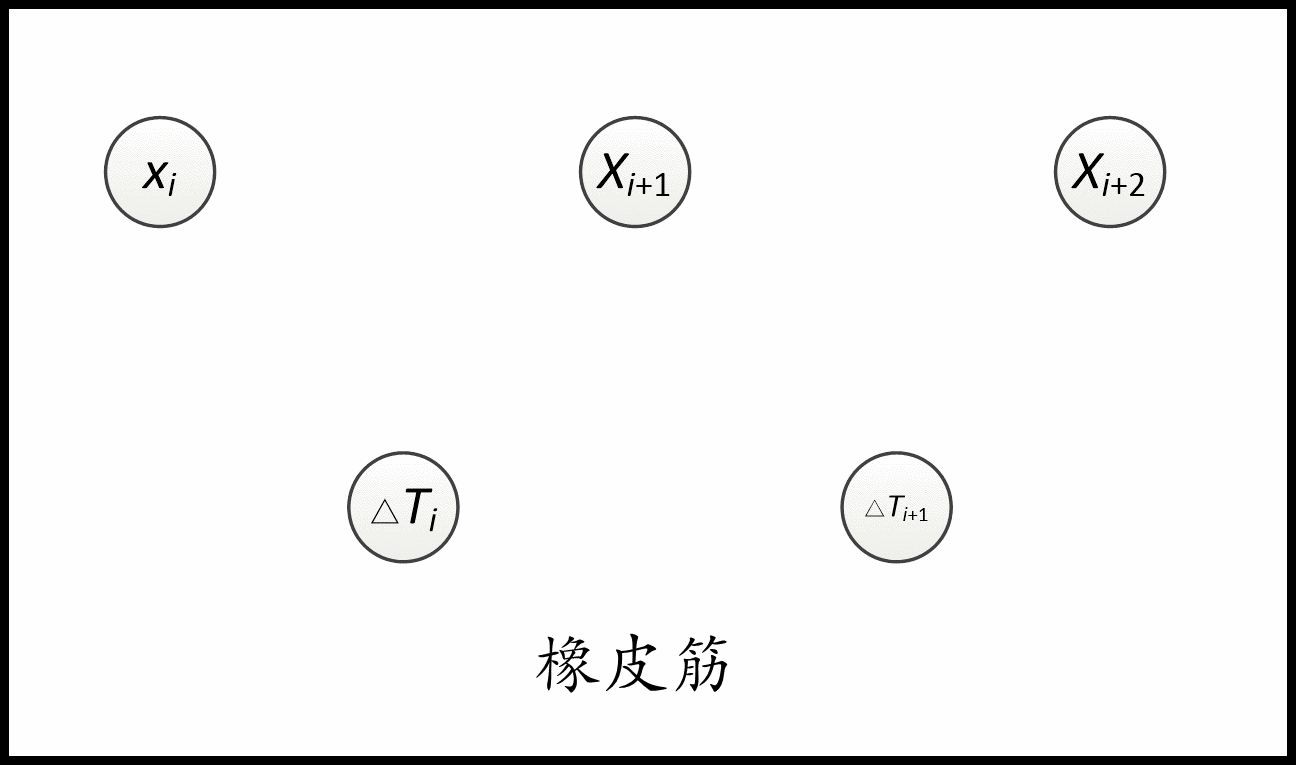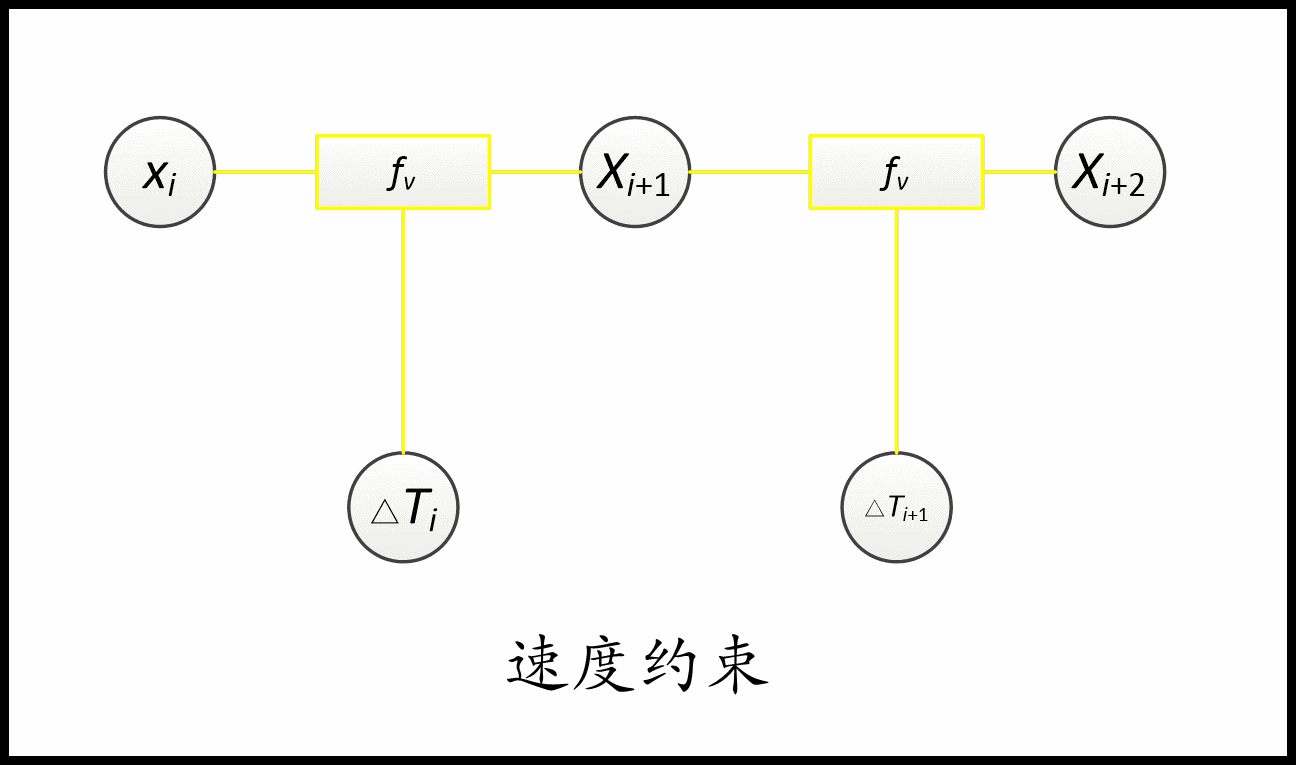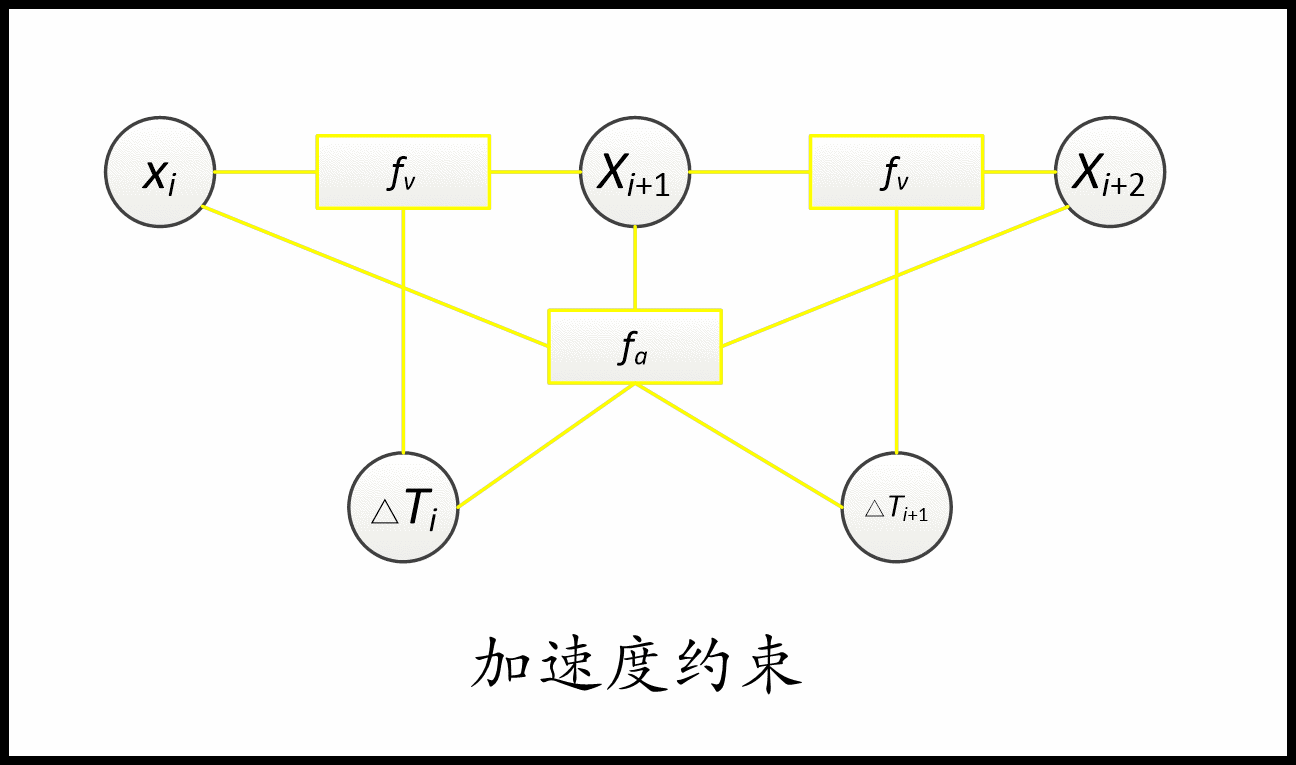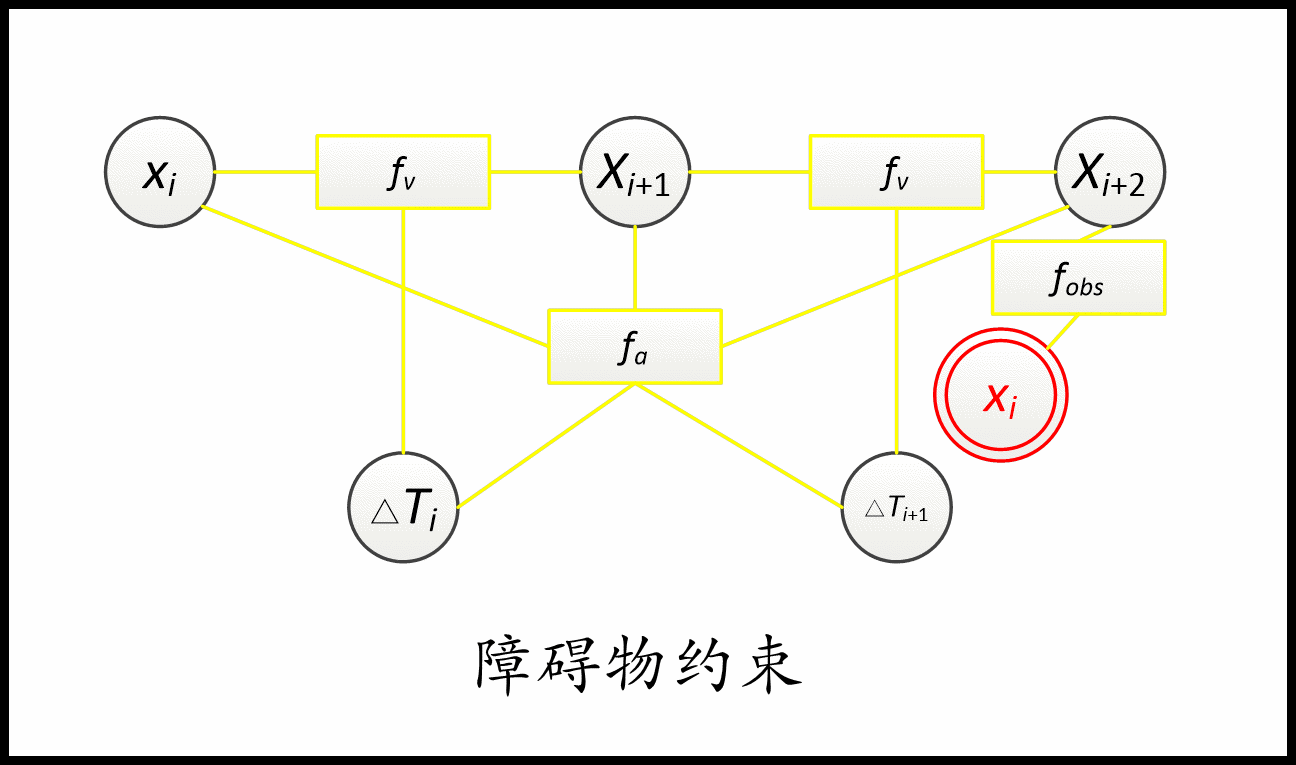
平时所说的图优化的最小二乘形式是这样的:
TEB所优化的目标函数是这样的:
我们先把上面的F(x)看成 , 其中
图优化中,顶点是待估计的参数,观测数据构成了边。 TEB的待估计参数就是 ,也就是位姿和时间差的组合。 边表示目标函数 ,并连接多个顶点。
这个图的顶点vertexs是橡皮筋的状态(机器人姿态+时间),起点和终点当然是固定的,图的边是我们自己定义的优化目标函数。默认使用利文伯格法,优化器是g2o::CSparse
g2o框架在批处理模式下优化了TEB,因此每次迭代都会生成一个新的图。在一个机器人控制周期内对轨迹修改步骤进行多次迭代(四个循环包括5次利文伯格的迭代)。 g2o框架提供了两种基于Cholesky decomposition 的求解器: CHOLMOD 和 CSparse。默认是CSParse
对优化后的TEB进行验证,检查是否违反了硬约束,如果违反,在这种情况下机器人要么停止,要么重新调用运动规划器。
TEB每次迭代的平均运行时间依赖于TEB的维数,TEB的维数随位姿数(configurations)线性增长。对于10000多个states,对应大约2500种configurations。
TEB中实现了两种规划器,一个就是普通的TebOptimalPlanner,另一个是HomotopyClassPlanner,HomotopyClassPlanner是一种同时优化多个轨迹的方法,由于目标函数的非凸性(非凸函数)会生成一系列最优的候选轨迹,最终在备选局部解的集合中寻求总体最佳候选轨迹,对应论文:《Integrated online trajectory planning and optimization in distinctive topologies》
optimizer本身只能找到局部最优轨迹,有时找到的路径invalid,所以一般都是用HomotopyClassPlanner。HomotopyClassPlanner类像是多个TebOptimalPlanner类实例的组合。HomotopyClassPlanner类中也会实例化一个由全局规划器生成的路径作为参考的对象。除此之外,它还会使用probabilistic roadmap (PRM) methods在障碍物周边采样一些keypoints,将这些keypoints连接起来,去除方向没有朝向目标点的连接和与障碍物重叠的连接。这样就形成了一个网络,然后将起始点和终点接入到这个网络。如下图所示: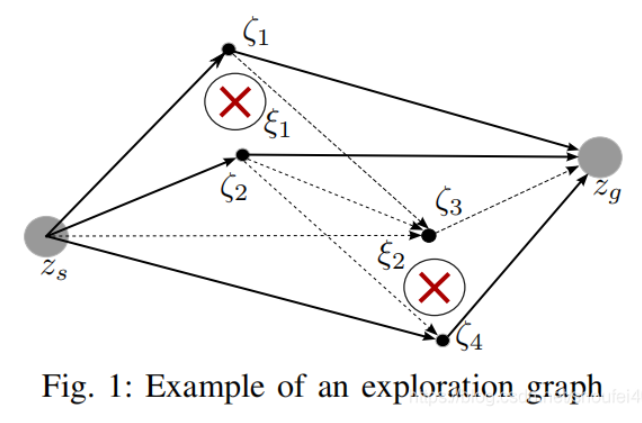
使用Depth First Search(深度优先方法)搜索所有可行的路径。将这些路径作为参考,实例化多个TebOptimalPlanner类的实例。采用多线程并行优化,得到多条优化后的路径。将这些路径进行可行性分析,选出代价值最小的最优路径。不得不说HomotopyClassPlanner类里的方法是一个鲁棒性和可靠性更高的方法。
编译teb时报错,或者在没有编译TEB的计算机上通过.so运行TEB时会报错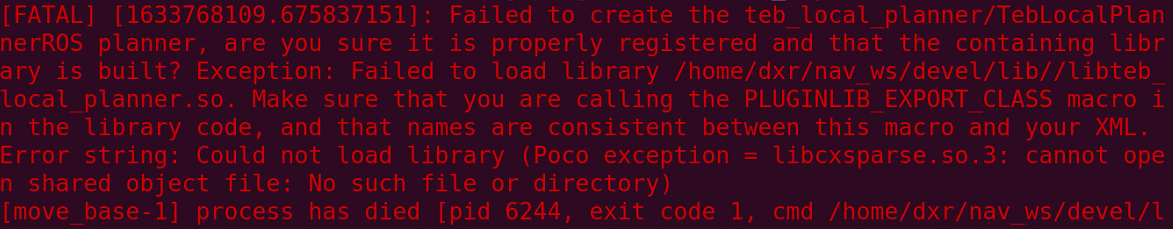
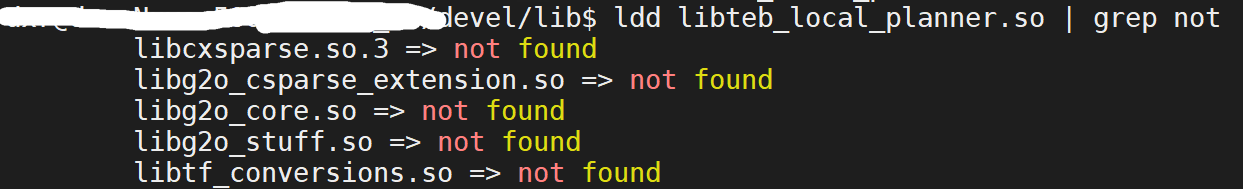
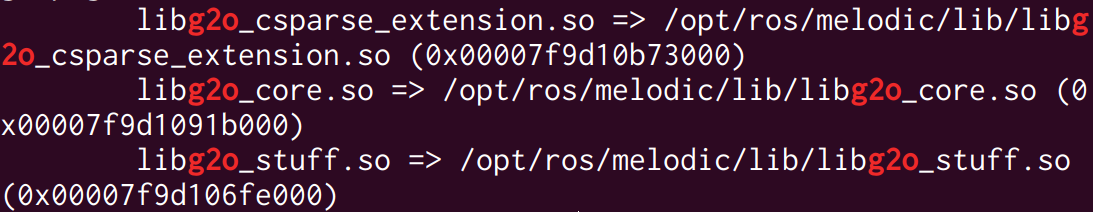
因为没有安装g2o和ceres,不过不需要自己安装g2o。 先运行sudo apt-get install ros-melodic-teb-local-planner,这样会在/opt/ros里安装g2o,然后把g2o的so文件复制到/usr/local/lib1
2sudo cp /opt/ros/melodic/lib/libg2o* /usr/local/lib
sudo cp -r /opt/ros/melodic/include/g2o /usr/local/include
如果自己之前安装的g2o的相关共享库没有清除干净,解决方法为:
sudo rm -rf /usr/local/include/g2o/usr/local/lib下有关libg2o*.so的库文件,先进入目录/usr/local/lib,然后挨个(可多个同时)删除: `sudo rm -rf libg2o.so libg2o_.so libg2o_*.so`ROS2环境下,安装TEB算法1
2
3
4
5git clone https://github.com/rst-tu-dortmund/costmap_converter.git -b ros2
git clone https://github.com/rst-tu-dortmund/teb_local_planner.git -b ros2-master
cd ~/catkin_ws
rosdep install -i --from-path src --rosdistro galactic -y
参考:
对ROS局部运动规划器Teb的理解
Trajectory modification considering dynamic constraints of autonomous robots
Efficient Trajectory Optimization using a Sparse Model—使用稀疏模型对有效轨迹进行优化
L2范数 squareNorm(),等价于计算vector的自身点积,norm()返回squareNorm的开方根。
这些操作应用于matrix,norm() 会返回Frobenius或Hilbert-Schmidt范数。
如果你想使用其他Lp范数,可以使用lpNorm< p >()方法。p可以取Infinity,表示L∞范数1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20int main()
{
VectorXf v(2);
MatrixXf m(2,2), n(2,2);
v << -1,
2;
m << 1,-2,
-3,4;
cout << "v.squaredNorm() = " << v.squaredNorm() << endl;
cout << "v.norm() = " << v.norm() << endl;
cout << "v.lpNorm<1>() = " << v.lpNorm<1>() << endl;
cout << "v.lpNorm<Infinity>() = " << v.lpNorm<Infinity>() << endl;
cout << endl;
cout << "m.squaredNorm() = " << m.squaredNorm() << endl;
cout << "m.norm() = " << m.norm() << endl;
cout << "m.lpNorm<1>() = " << m.lpNorm<1>() << endl;
cout << "m.lpNorm<Infinity>() = " << m.lpNorm<Infinity>() << endl;
}
rostopic echo move_base/status
1 | rostopic pub /move_base_simple/goal geometry_msgs/PoseStamped "header: |
一句话:rostopic pub /move_base/cancel actionlib_msgs/GoalID -- {},即向话题/move_base/cancel发空消息1
2
3
4ros::Publisher cancle_pub_ = nh_.advertise("move_base/cancel",1);
actionlib_msgs::GoalID first_goal;
cancle_pub_.publish(first_goal);
1 | install(TARGETS node |
最终的可执行文件的路径在install/lib/node
另一种情况,test_node是可执行文件,test是动态库,target_link_libraries只是保证了devel/lib/test_node中的可执行文件链接了test,但不保证install/lib/test_node中链接了test,需要如下配置1
2
3
4
5
6install(
TARGETS test test_node
ARCHIVE DESTINATION ${CATKIN_PACKAGE_LIB_DESTINATION}
LIBRARY DESTINATION ${CATKIN_PACKAGE_LIB_DESTINATION}
RUNTIME DESTINATION ${CATKIN_PACKAGE_BIN_DESTINATION}
)
注意,如果修改了test对应的源文件, 需要把编译后的libtest.so也更新到远程机,否则test_node没有变化
CMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX变量类似于configure脚本的–prefix,常见的使用方法是在build文件夹里执行cmake -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=/usr ..
INSTALL指令用于定义安装规则,安装的内容可以包括目标二进制、动态库、静态库以及
文件、目录、脚本等。
检查CMakelist文件发现路径是include_directories("/usr/include/eigen3")
检查eigen3的路径,发现我的是/usr/local/include/eigen3/Eigen,可以链接对应的文件,即进行以下命令:1
sudo ln -s /usr/local/include/eigen3/Eigen /usr/include/Eigen
sudo ln -s 源文件 目标文件是一个常用的linux命令,功能是为源文件在目标文件的位置建立一个同步的链接,当二者建立联系后即可在源文件中访问目标文件。
链接有两种,一种被称为硬链接(Hard Link),另一种被称为符号链接(Symbolic Link). 建立硬链接时,链接文件和被链接文件必须位于同一个文件系统中,并且不能建立指向目录的硬链接。默认情况下,ln产生硬链接。如果给ln命令加上- s选项,则建立符号链接。
把所有配置放到文件g2o.cmake,然后在CMakeLists里添加1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8set(ALL_TARGET_LIBRARIES "")
include(g2o.cmake)
# 最后添加
target_link_libraries(${PROJECT_NAME}
${catkin_LIBRARIES}
${ALL_TARGET_LIBRARIES}
)
无需再添加eigen的头文件目录
我目前用的还是g2o旧版本,如果程序对应的是新版本,可能出现这样的报错1
error: ‘make_unique’ is not a member of ‘g2o’
g2o的CMakeLists.txt的OpenMP部分1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12# Eigen parallelise itself, OPENMP is experimental. We experienced some slowdown with it
set(G2O_USE_OPENMP OFF CACHE BOOL "Build g2o with OpenMP support (EXPERIMENTAL)")
if(G2O_USE_OPENMP)
find_package(OpenMP)
if(OPENMP_FOUND)
MESSAGE(" ----------------- Using OpenMP ! ----------------- ")
set (G2O_OPENMP 1)
set(g2o_C_FLAGS "${g2o_C_FLAGS} ${OpenMP_C_FLAGS}")
set(g2o_CXX_FLAGS "${g2o_CXX_FLAGS} -DEIGEN_DONT_PARALLELIZE ${OpenMP_CXX_FLAGS}")
message(STATUS "Compiling with OpenMP support")
endif(OPENMP_FOUND)
endif(G2O_USE_OPENMP)
使用OpenMP编译安装g2o,即set(G2O_USE_OPENMP ON),但是随即编译我的程序报错:1
2
3/usr/bin/ld: CMakeFiles/ls_slam_g2o.dir/src/main.cpp.o: undefined reference to symbol 'omp_set_lock@@OMP_3.0'
//usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libgomp.so.1: error adding symbols: DSO missing from command line
collect2: error: ld returned 1 exit status
搜索发现函数void lock() { omp_set_lock(&_lock); } 定义在 openmp_mutex.h
在CMakeLists.txt中添加:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8FIND_PACKAGE(OpenMP)
target_link_libraries(node
${catkin_LIBRARIES}
${CSPARSE_LIBRARY}
${G2O_LIBS}
OpenMP::OpenMP_CXX
)
CMakeLists.txt如下1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8.3)
project(node)
add_compile_options(-std=c++11)
set(CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE "Realease")
LIST(APPEND CMAKE_MODULE_PATH ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/cmake_modules)
# find g2o lib
find_package(G2O REQUIRED)
IF(G2O_FOUND)
include_directories(${G2O_INCLUDE_DIR})
message(" -------- G2O lib is found-------- : "${G2O_INCLUDE_DIR})
ENDIF(G2O_FOUND)
find_package(Eigen3 REQUIRED)
find_package(CSparse REQUIRED)
find_package(catkin REQUIRED COMPONENTS
roscpp
rospy
std_msgs
)
# g2o的库文件也可能在 /usr/local/lib
LINK_DIRECTORIES(/opt/ros/melodic/lib)
SET(G2O_LIBS g2o_cli g2o_ext_freeglut_minimal g2o_simulator g2o_solver_slam2d_linear g2o_types_icp g2o_types_slam2d g2o_core g2o_interface g2o_solver_csparse g2o_solver_structure_only g2o_types_sba g2o_types_slam3d g2o_csparse_extension g2o_opengl_helper g2o_solver_dense g2o_stuff g2o_types_sclam2d g2o_parser g2o_solver_pcg g2o_types_data g2o_types_sim3 cxsparse )
catkin_package(
# INCLUDE_DIRS include
# LIBRARIES ls_slam
# CATKIN_DEPENDS roscpp rospy std_msgs
# DEPENDS system_lib
)
include_directories(
include
${catkin_INCLUDE_DIRS}
${EIGEN_INCLUDE_DIRS}
${CSPARSE_INCLUDE_DIR}
)
add_executable(node src/main.cpp)
target_link_libraries(node ${catkin_LIBRARIES} ${CSPARSE_LIBRARY} ${G2O_LIBS})
编译g2o结果报错fatal error: Eigen/Core: No such file or directory
compilation terminated.
FindEigen3.cmake 使用以下代码段:1
2
3
4
5
6find_path(EIGEN3_INCLUDE_DIR NAMES signature_of_eigen3_matrix_library
PATHS
${CMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX}/include
${KDE4_INCLUDE_DIR}
PATH_SUFFIXES eigen3 eigen
)
所以它默认CMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX在Linux主机上查找/usr/local
打开可视化工具g2o_viewer和一个示例,如果能使用,就正常了
manhattan3500 dataset
1 | class OdometryHelperRos { |
这是base_local_planner局部规划器里起辅助功能的一个类,主要作用就是从/odom的topic中获取机器人的速度状态(包括线速度(x,y)和角速度z)
Costmap2DROS类有一个成员base_local_planner::OdometryHelperRos odom_helper_;,提供给用户获取当前机器人速度的接口
要使用,首先#include <base_local_planner/odometry_helper_ros.h>,
OdometryHelperRos()在初始化的时候,新建了NodeHandle并设置关注的topic的名称odom_topic;
并在回调函数odomCallback()中, 取出速度信息
类TrajectoryPlannerROS中定义: base_local_planner::OdometryHelperRos odom_helper_;
move_base的yaml中,对局部路径规划配置:teb_local_planner/TebLocalPlannerROS
MoveBase中有一段:1
2
3private_nh.param("base_local_planner", local_planner, std::string("base_local_planner/TrajectoryPlannerROS"));
tc_ = blp_loader_.createInstance(local_planner);
tc_->initialize(blp_loader_.getName(local_planner), &tf_, controller_costmap_ros_);
1 | tf::Stamped<tf::Pose> robot_vel_tf; |
1 | bool stopped(const nav_msgs::Odometry& base_odom, |
CostmapModel类继承了WorldModel,能够获取点、连线、多边形轮廓的cost,是局部规划器与costmap间的一个桥梁。初始化在move_base的构造函数,一般如下使用:1
2
3
4//costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS* planner_costmap_ros_
world_model_ = new base_local_planner::CostmapModel(*(planner_costmap_ros_ ->getCostmap()) );
std::vector<geometry_msgs::Point> footprint = planner_costmap_ros_->getRobotFootprint();
double footprint_cost = world_model_->footprintCost(x_i, y_i, theta_i, footprint);CostmapModel类帮助local planner在Costmap上进行计算, footprintCost, lineCost, pointCost三个类方法分别能通过Costmap计算出机器人足迹范围、两个cell连线、单个cell的代价,并将值返回给局部规划器。
原型1
2
3
4
5double base_local_planner::CostmapModel::footprintCost(const geometry_msgs::Point & position,
const std::vector< geometry_msgs::Point > & footprint,
double inscribed_radius,
double circumscribed_radius
)
Checks if any obstacles in the costmap lie inside a convex footprint that is rasterized into the grid.
参数:
返回值:
Positive if all the points lie outside the footprint, negative otherwise: -1 if footprint covers at least a lethal obstacle cell, or -2 if footprint covers at least a no-information cell, or -3 if footprint is [partially] outside of the map
footprintCost函数,先调用WorldModel类里面的footprintCost函数,用x,y,th把footprint_spec变成世界坐标下坐标,还得到原点在世界坐标系坐标,内切半径,外切半径。根据这些,调用CostmapModel::footprintCost函数,转换到costmap坐标系下,用光栅化算法得到栅格点,由栅格点的代价值得到足迹点线段的代价值,再得到整个足迹点集的代价值就可以了。
footprintCost函数为提高效率,它不计算足迹所有栅格的代价,认为只要计算N条边涉及到的栅格,就可计算出最大代价。首先尝试获取线段的地图坐标,然后利用lineCost函数计算线段代价值,并用footprint_cost参数保存最大的线段代价值,最终如果正常,则返回的也是footprint_cost。只要有1个线段的代价值小于0,则直接返回-1。
注意函数和栅格计算的代价值不同:返回值中,最大值是253, 即INSCRIBED_INFLATED_OBSTACLE,因为比253大的 LETHAL_OBSTACLE (254), NO_INFORMATION (255)会分别返回-1、-2,表示不可行。
返回值:
没有撞障碍时,返回值是 0
函数原型对第一个参数position的解释是:The position of the robot in world coordinates。实际是 局部代价地图的全局坐标系 ,一般是 map 或 odom
以tf::Stamped<tf::Pose>为输入类型1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27tf::Stamped<tf::Pose> input_pose;
input_pose.setOrigin(tf::Vector3(x, y, 0) );
input_pose.setRotation(tf::createQuaternionFromYaw(theta) );
input_pose.frame_id_ = "map";
input_pose.stamp_ = ros::Time::now();
tf::Stamped<tf::Pose> global_pose_in_local_costmap;
auto tf = context_->tf_;
try
{
tf->transformPose( local_planner_costmap_ros_->getGlobalFrameID(),
input_pose,
global_pose_in_local_costmap);
}
catch (tf::TransformException& ex)
{
ROS_INFO("Cannot transform in inCollision !");
return false;
}
double temp_x = global_pose_in_local_costmap.getOrigin().getX();
double temp_y = global_pose_in_local_costmap.getOrigin().getY();
double footprint_cost = world_model_->footprintCost(
temp_x,
temp_y,
tf::getYaw(global_pose_in_local_costmap.getRotation() ),
local_costmap_ros->getRobotFootprint() );
1 | double CostmapModel::footprintCost(const geometry_msgs::Point& position, |
搜索发现有3个lineCost函数, TrajectoryPlanner::lineCost, VoxelGridModel::lineCost, CostmapModel::lineCost。经过运行,发现调用的还是CostmapModel::lineCost
对于线段的代价计算函数lineCost,其实是对线段中的所有像素点(通过bresenham算法得到,不必深入研究)进行代价计算,如果像素点的代价为LETHAL_OBSTACLE或者NO_INFORMATION,则该点代价为-1。如果某个点的代价为-1,则该线段的代价也为-1,否则取所有点中最大的代价作为线段的代价1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28// return a positive cost for a legal line 或者负值
double CostmapModel::lineCost(int x0, int x1, int y0, int y1) const
{
double line_cost = 0.0;
double point_cost = -1.0;
for( LineIterator line( x0, y0, x1, y1 ); line.isValid(); line.advance() )
{
point_cost = pointCost( line.getX(), line.getY() );
if(point_cost < 0)
return point_cost;
if(line_cost < point_cost)
line_cost = point_cost;
}
return line_cost;
}
double CostmapModel::pointCost(int x, int y) const
{
unsigned char cost = costmap_.getCost(x, y);
//if the cell is in an obstacle the path is invalid
if(cost == NO_INFORMATION)
return -2;
if(cost == LETHAL_OBSTACLE)
return -1;
return cost;
}
参考:
CostmapModel::footprintCost
ObstacleCostFunction类,继承自Trajectory类