configureBackupModes 第二部分
1 | // detect and resolve oscillations |
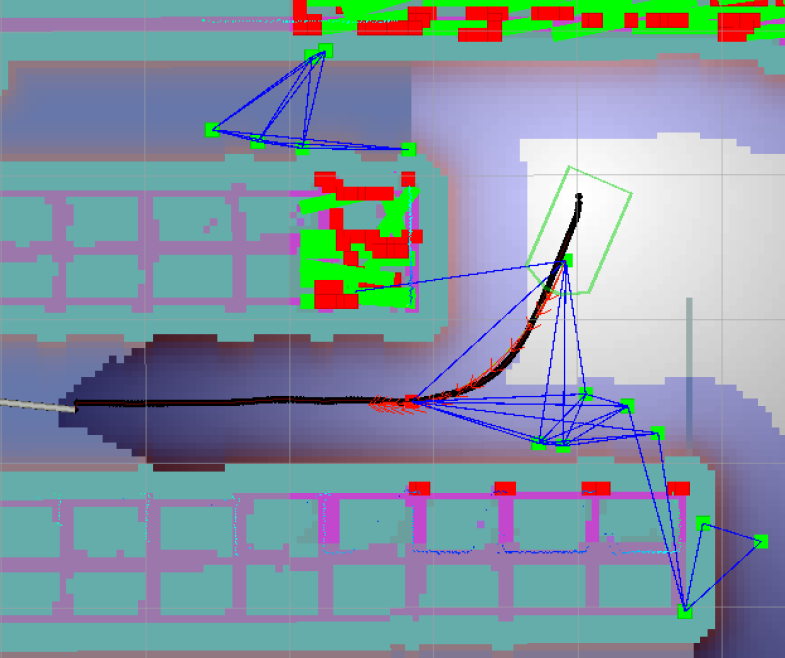
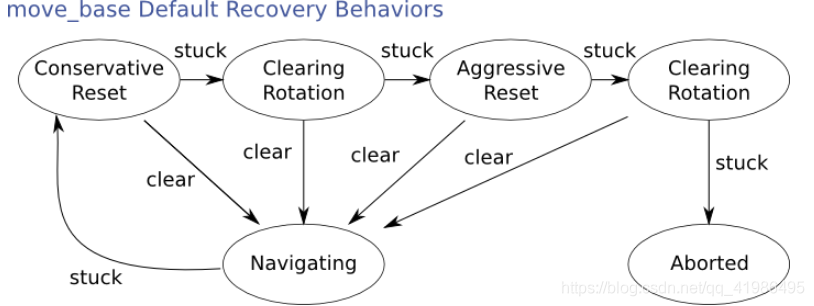
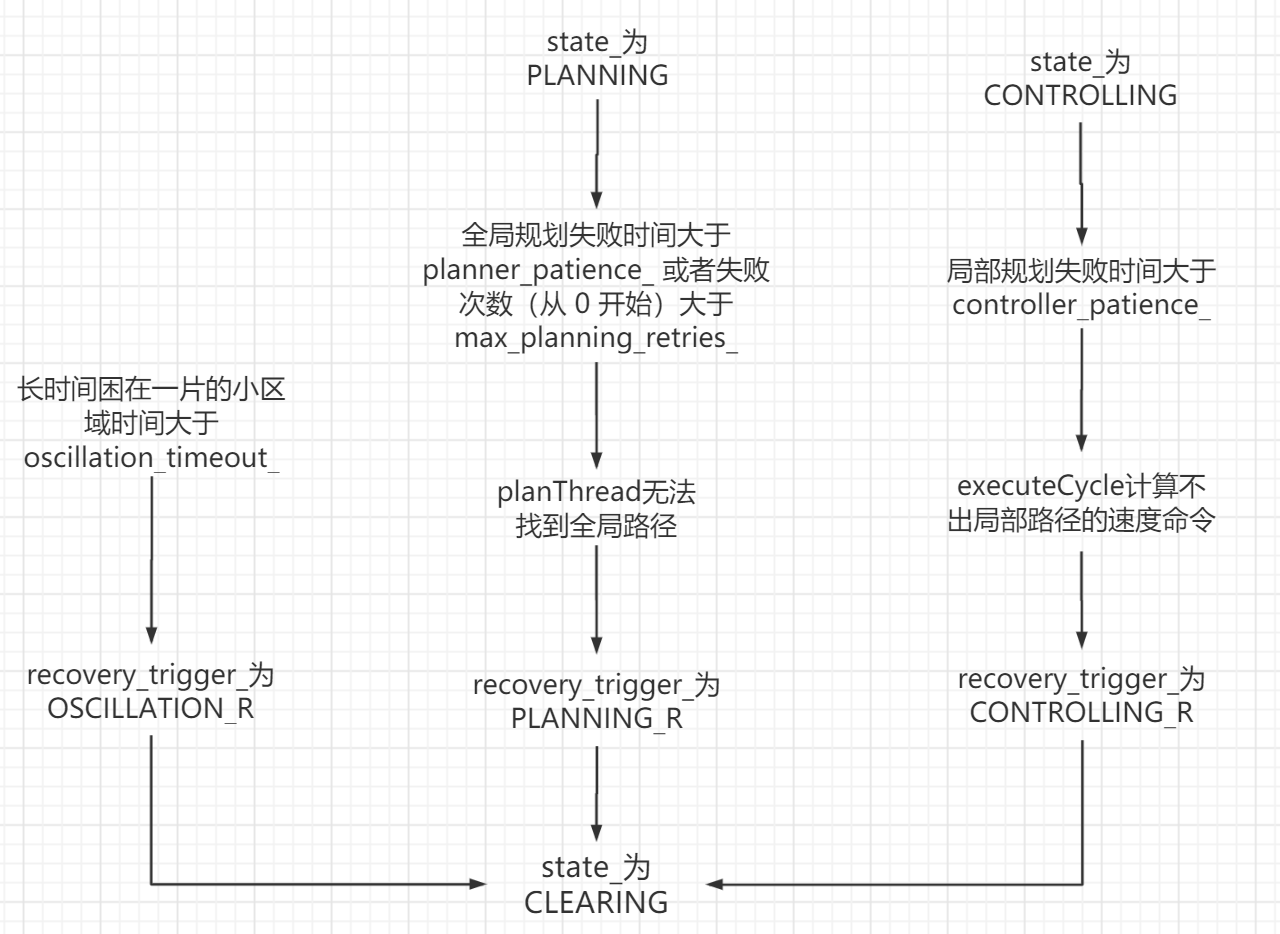
但是如果机器人确实stucked,最终会在move_base里Abort
setPreferredTurningDir
设置期望的初始转弯方向 (也就是惩罚相反的方向)。A desired (initial) turning direction might be specified in case the planned trajectory oscillates between two solutions (in the same equivalence class!) with similar cost. 配置参数以调整惩罚的权重,Initial 说明惩罚只适用于trajectory的前几个位姿
参数dir可以是RotType::left, RotType::right, RotType::none
代码实际调用的是:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8void HomotopyClassPlanner::setPreferredTurningDir(RotType dir)
{
// set preferred turning dir for all TEBs
for (TebOptPlannerContainer::const_iterator it_teb = tebs_.begin(); it_teb != tebs_.end(); ++it_teb)
{
(*it_teb)->setPreferredTurningDir(dir);
}
}
结果还是TebOptimalPlanner的同名成员函数,赋值而已1
virtual void setPreferredTurningDir(RotType dir) { prefer_rotdir_ = dir; }
赋值完了,prefer_rotdir_会在AddEdgesPreferRotDir里产生影响
AddEdgesPreferRotDir
1 | void TebOptimalPlanner::AddEdgesPreferRotDir() |
调用时在configureBackupModes第二部分,那里是对prefer_rotdir_赋值,
FailureDetector
类FailureDetector的代码在TEB的recovery_behaviors.cpp,FailureDetector检测机器人是否 stucked或者振荡,分析last N(buffer的大小)个速度命令,看这些线速度和角速度的平均值是否小于oscillation_v_eps 和 oscillation_omega_eps
构造函数和析构全是空。
buffer
1 | // Set buffer length (measurement history) |
调用:1
2failure_detector_.setBufferLength(std::round(
cfg_.oscillation_filter_duration * controller_frequency ) );
默认是10*30,其实比较大,可以降低oscillation_filter_duration
1 | // Clear buffer, 置为不振荡状态 |
FailureDetector::update
先看调用,只有第一个参数是速度控制量,其他都是配置参数:1
2
3
4failure_detector_.update(last_cmd_, cfg_.robot.max_vel_x, cfg_.robot.max_vel_x_backwards,
max_vel_theta, cfg_.recovery.oscillation_v_eps, cfg_.recovery.oscillation_omega_eps);
bool oscillating = failure_detector_.isOscillating();
源码其实也简单1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26void FailureDetector::update(const geometry_msgs::Twist& twist, double v_max, double v_backwards_max, double omega_max, double v_eps, double omega_eps)
{
if (buffer_.capacity() == 0)
return;
VelMeasurement measurement;
/*
struct VelMeasurement
{
double v = 0;
double omega = 0;
}; */
measurement.v = twist.linear.x; // 不考虑 y 方向速度
measurement.omega = twist.angular.z;
if (measurement.v > 0 && v_max>0)
measurement.v /= v_max;
else if (measurement.v < 0 && v_backwards_max > 0)
measurement.v /= v_backwards_max;
if (omega_max > 0)
measurement.omega /= omega_max;
buffer_.push_back(measurement);
// immediately compute new state
detect(v_eps, omega_eps);
}
detect
v_eps: (0,1)内的normalized 线速度的平均值的阈值,默认0.1omega_eps: (0,1)内的normalized 角速度的平均值,默认0.1
如果机器人stucked则返回true,否则false1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27bool detect(double v_eps, double omega_eps)
{
oscillating_ = false;
//至少有一半的速度数据才检测,也就是过一点时间才判断
if (buffer_.size() < buffer_.capacity()/2)
return false;
double n = (double)buffer_.size();
// 计算buffer内线速度和角速度的均值
double v_mean=0;
double omega_mean=0;
int omega_zero_crossings = 0;
for (int i=0; i < n; ++i)
{
v_mean += buffer_[i].v;
omega_mean += buffer_[i].omega;
if ( i>0 && g2o::sign(buffer_[i].omega) != g2o::sign(buffer_[i-1].omega) )
++omega_zero_crossings;
}
v_mean /= n;
omega_mean /= n;
if (std::abs(v_mean) < v_eps && std::abs(omega_mean) < omega_eps
&& omega_zero_crossings>1 )
{
oscillating_ = true;
}
return oscillating_;
}
参数
我用的参数值如下:1
2
3
4
5
6
7shrink_horizon_backup = true;
shrink_horizon_min_duration = 10: # 默认10
oscillation_recovery = true;
oscillation_v_eps = 0.1; # 线速度和角速度设置0.1已经足够
oscillation_omega_eps = 0.1;
oscillation_recovery_min_duration = 5;
oscillation_filter_duration = 6 # 默认10,这个大了会使buffer太大
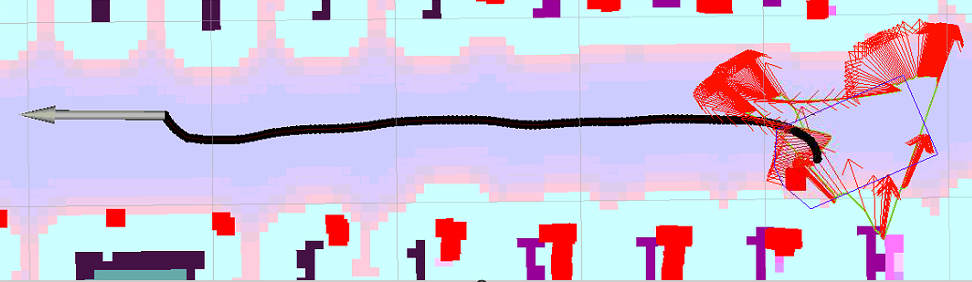
要出现振荡,最直观的就是车左右摇摆或者车前后小步行走,因为代码中没有绝对值,否则朝一个方向小幅行走也算振荡了。实际中当然是不允许这种奇怪的行为。